Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a technology that allows users to access a desktop or application hosted on a remote server over a network connection. In simple words, it control another computer from a different location.
This service is part of the Windows Server system and is widely used in businesses to enable secure, flexible, and efficient remote working environments.

How Does Remote Desktop Services Work?
RDS works on a client-server model:
- The server hosts the applications, files, and computing resources.
- The client (your device) connects to the server through a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) connection.
Once connected, you see the server’s desktop on your screen and can use applications, open files, and perform tasks — all processed on the remote system, not your local machine.
Key Components of Remote Desktop Services
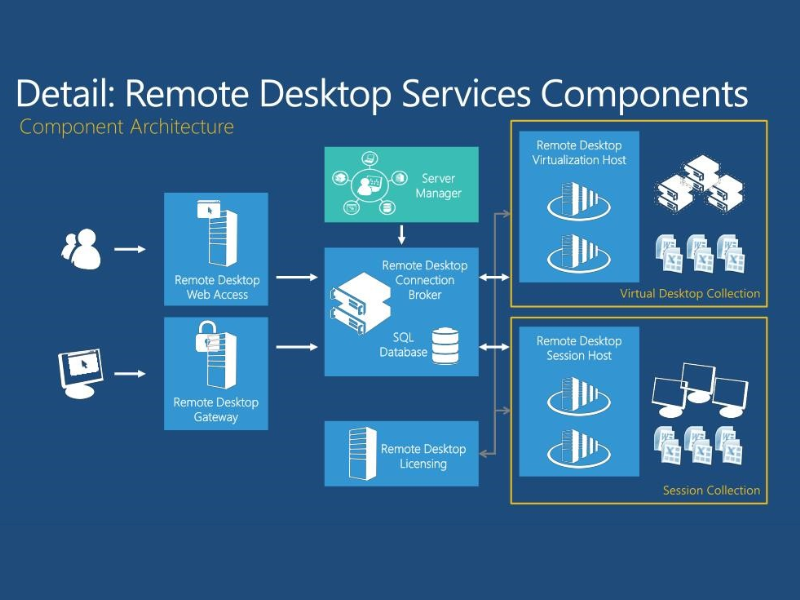
To understand how RDS operates, here are its main components:
- Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH): Hosts Windows-based programs or desktops for users to access.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RDCB): Manages user sessions and reconnects users to their existing sessions.
- Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway): Allows users to securely connect from outside the corporate network.
- Remote Desktop Web Access (RD Web Access): Provides browser-based access to applications and desktops.
- Remote Desktop Licensing (RD Licensing): Manages RDS Client Access Licenses (CALs) for users or devices.
Benefits of Remote Desktop Services
Here are some of the top advantages businesses gain from RDS:
1. Work From Anywhere
Employees can securely access their desktops and data from any device and any location with internet connectivity.
2. Centralized Management
All applications and data are hosted in one place, making updates, backups, and security management easier for IT teams.
3. Enhanced Security
Since data never leaves the server, RDS minimizes data breach risks and allows administrators to enforce strict access controls.
4. Cost Efficiency
Instead of upgrading individual computers, businesses can use RDS to deliver apps and desktops from a centralized server — reducing hardware and maintenance costs.
5. Scalability
As your organization grows, it’s easy to add new users or expand computing power without major infrastructure changes.
Use Cases of Remote Desktop Services
RDS is useful across various industries and scenarios, such as:
- IT Support: Technicians can remotely troubleshoot and resolve issues.
- Call Centers: Centralized access to software applications and customer databases.
- Education: Students and teachers can access virtual labs and learning resources remotely.
- Finance & Healthcare: Secure remote access to sensitive data and compliance-driven systems.
Conclusion
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, enabling secure remote access, simplified management, and cost savings for organizations of all sizes. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, IT manager, or remote worker, understanding RDS can help you build a smarter, more connected workplace.